Application of the STAS Scale: Window of Tolerance and Dysregulation in C-PTSD with Dependence. Neuro-Psycho-Biological and Clinical Analysis: The Defensive Performer.
AUTHORS: Massimo Lattanzi, Tiziana Calzone (AIPC, ONOF, CIPR)
INTRODUCTION This work is the result of a synergistic collaboration between high-level training institutions and clinical research entities within the Italian landscape. AIPC (Italian Association for Clinical Psychoanalysis and Applied Research) is configured as a study hub for the integration of psychodynamic models and modern acquisitions in affective neuroscience. ONOF (National Observatory on Family Homicides) provides methodological support for mapping higher mental processes and their functional alterations. Finally, CIPR (Italian Center for Relational Psychotraumatology), with its operational branches, represents the clinical arm where theoretical models are translated into intervention protocols for complex pathologies. The partnership between these realities aims to define new diagnostic standards for understanding contemporary psychopathology.
ABSTRACT This scientific contribution illustrates the application of the STAS diagnostic framework (History, Trauma, Attachment, Strategy/Symptom) in the analysis of a complex case of Complex Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (C-PTSD, ICD-11: 6B41) comorbid with stimulant use disorder. The objective is to map the neurobiological functioning of the subject, identified as a "defensive performer," focusing on alterations in the Window of Tolerance and the management of allostatic load resulting from chronic stress. Through the multidimensional analysis of STAS variables, it is highlighted how social performance and substance use (cocaine) are not hedonistic behaviors, but dysfunctional attempts at a regulatory prosthesis to avoid collapsing into states of hypo-arousal (shame, emptiness) deriving from an invalidating developmental environment. The paper describes the oscillatory dynamic between sympathetic hyper-arousal and systemic collapse, proposing a psychopathological synthesis aimed at rehabilitating neural co-regulation skills.
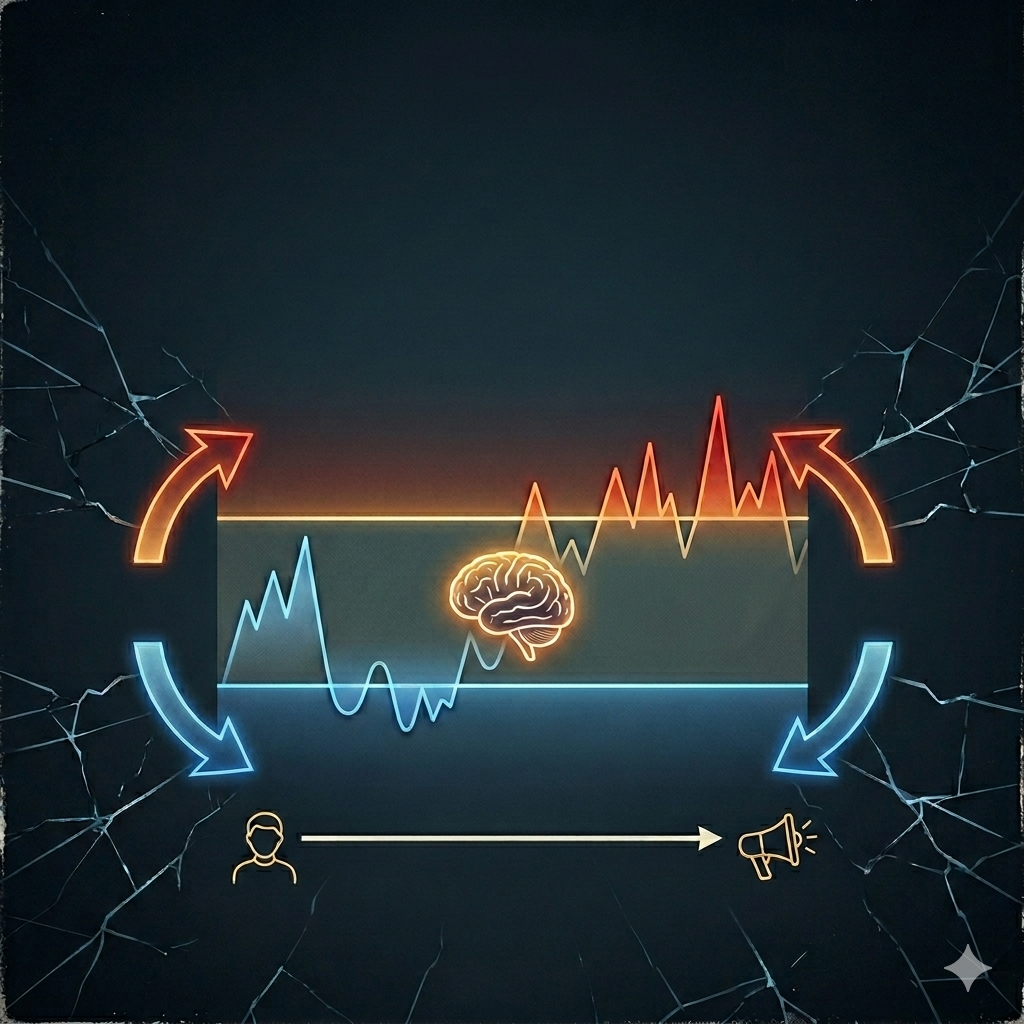
INTRODUCTION TO THE INSTRUMENT: THE STAS SCALE The STAS Scale is configured as an advanced diagnostic framework designed to map the structure of the subject's neurobiological functioning. The instrument is not limited to descriptive nosography but analyzes the dynamic interaction between five crucial dimensions to determine the functional width of the "Window of Tolerance" (Siegel, 1999) and the often pathological modes of managing cumulative allostatic load.
The variables under investigation are:
- S - History (Storia): Analysis of developmental anamnesis and the environmental context of development, with a focus on the dichotomy between invalidating and validating environments.
- T - Trauma: Mapping of specific threat events ("Big-T") and cumulative neglect ("small-t") responsible for the permanent alteration of the amygdala activation threshold.
- A - Attachment (Attaccamento): Assessment of the quality of neural circuits responsible for interpersonal safety and the acquired capacity for dyadic co-regulation.
- S - Strategy (Defensive) & Symptom/Substance: Identification of structured neuro-behavioral adaptations (e.g., False Self, Hyper-performance) necessary for psychic survival in the presence of regulatory deficits. Reading of dysfunctional behavior (e.g., use of psychostimulants) as a self-produced pharmacological attempt to artificially re-enter the window of tolerance.
CLINICAL CASE: THE SUBJECT ALESSANDRO
Demographic and Nosographic Profile The subject, Alessandro (25 years old), a financial broker, presents a diagnosis of C-PTSD comorbid with stimulant use disorder. Clinical phenomenology highlights a phenotype defined as "defensive performer": a functioning characterized by a chronic exit from the window of tolerance towards the top (Hyper-arousal), socially masked by narcissistic traits of success and competence. This performance acts as a protective barrier against the potential collapse into states of Hypo-arousal, characterized by intolerable feelings of shame, emptiness, and powerlessness.
ANALYSIS OF STAS VARIABLES
Variables S/T: History and Trauma - The Etiopathogenesis of Regulatory Collapse The anamnesis reveals chronic exposure to an invalidating developmental environment, dominated by an authoritarian paternal figure. This context prevented the ontogenesis of effective self-regulation circuits. On a neurobiological level, systematic verbal humiliation was encoded not as a relational event, but as a threat to the survival of the Self, setting the autonomic nervous system on a constant alarm response. The structural consequence is a drastic reduction in the width of the window of tolerance and a functional deficit of the prefrontal cortex in modulating limbic activation ("You are weak"), resulting in pervasive emotional dysregulation.
Variable S (Symptom/Substance): The Regulatory Prosthesis The subject's use of cocaine does not pursue primary hedonistic goals. The substance acts as a pharmacological tool to manage intolerance to negative affective states.
- With Substance (False widening of the Window): The stimulant induces a state of controlled activation that the subject cognitively confuses with competence and self-efficacy. It is a "Euphoric Hyper-arousal" that allows for the active avoidance of depressive pain.
- Without Substance (Collapse into Hypo-arousal): In the absence of chemical support, the system precipitates below the window of tolerance, bringing out apathy, emotional anesthesia, toxic shame, and a sense of non-existence.
Oscillatory Dynamic and Variable A (Attachment) The clinical profile shows a violent alternation, without pause in the integration zone:
- "UP" Phase (Sympathetic Hyper-arousal): Dominance of the sympathetic nervous system, extreme vigilance focused on power, disconnection from bodily signals of fatigue (somatic alexithymia), and "mind blindness" towards the other (absence of empathy).
- "CRASH" Phase (Mixed Dysregulation): The exhausted system collapses chaotically. Paranoid hypervigilance remains even during the collapse, with impulse dyscontrol and reactive aggression as a desperate attempt at sympathetic ascent from the abyss of powerlessness.
This dynamic severely compromises Variable A. The relationship with the partner (Giulia) fails to serve as a "Secure Base" due to the absence, in the subject, of neural skills for co-regulation. The other is objectified: a tool to maintain euphoric activation in the UP phase, or a source of further stress in the DOWN phase.
PSYCHOPATHOLOGICAL SYNTHESIS AND THERAPEUTIC OBJECTIVE Alessandro's dysregulation graph shows the use of the substance as a "paradoxical stabilizer": the drug is used to "feel functional," but progressively erodes the residual capacity for natural self-regulation. The therapeutic goal, guided by the STAS analysis, is not simple abstinence, but working at the margins of the Window of Tolerance to gradually expand it. It is necessary to replace chemical regulation with somatic "grounding" strategies and, above all, with therapeutic co-regulation that allows for managing activation states without resorting to dissociation or the substance.
CONTACTS AND CLINICAL REFERENCES For further details on diagnostic protocols and to request specialist consultation based on the integrated model presented, readers and colleagues are invited to contact the operational branches of CIPR.
CIPR - Centro Italiano di Psicotraumatologia Relazionale (Italian Center for Relational Psychotraumatology) Pescara and Rome Branches
- Email: aipcitalia@gmail.com
- Website: www.associazioneitalianadipsicologiaecriminologia.it
- Phone/WhatsApp: 3924401930
Hashtag:
#italian center for relational psychotraumatology #femicide #national observatory on familial homicides #italian association of psychology and criminology #relational traumatic resonance #partner paradox #relational bubble #complex post-traumatic stress disorder